Swap space, also known as a swap file or swap partition, is a designated area on a computer's hard drive that is used as virtual memory by the operating system. When the physical RAM (Random Access Memory) of a system becomes full, the operating system moves less frequently accessed or idle data from the RAM to the swap space.
To create swap space on Debian 12, you can follow these steps:
Step 1 : Check the current disk usage and available space:

Ensure that you have sufficient disk space available to allocate for swap.
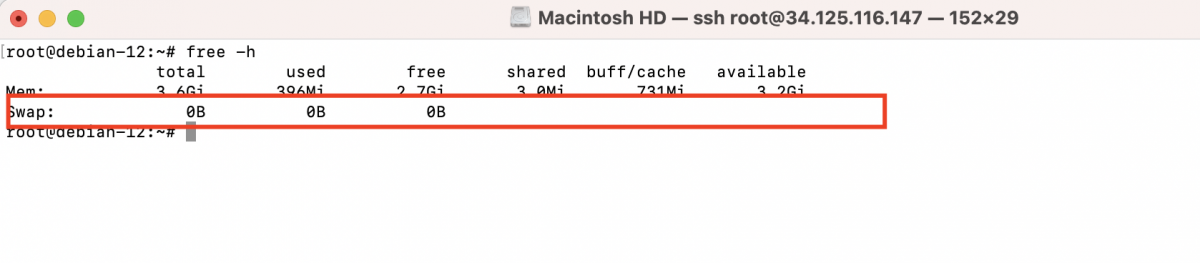
Step 2 : Check the current RAM size
Step 3 : Create a swap file:

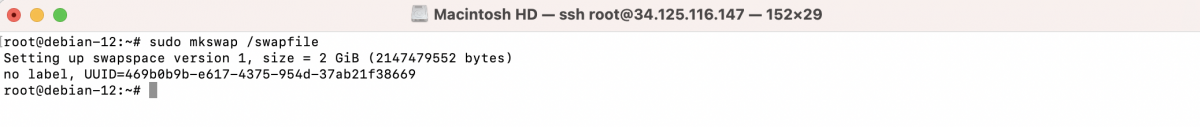
In this example, a 2GB swap file is created. Adjust the size as per your requirements.
Step 4 : Restrict the file permissions for security:

Step 5 : Set up the swap space:
Step 6 : Enable the swap file:

Step 7 : Verify that the swap space is enabled:
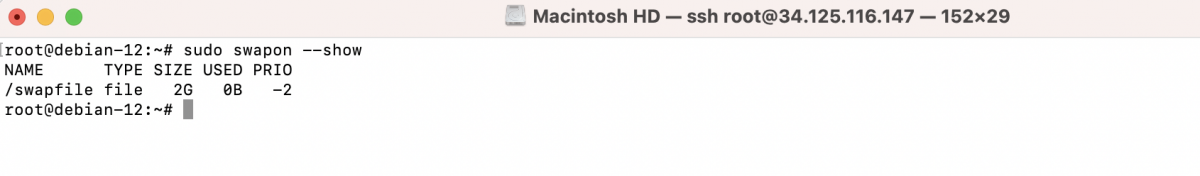
It should display the swap file information.
Step 8 : Make the swap space permanent:
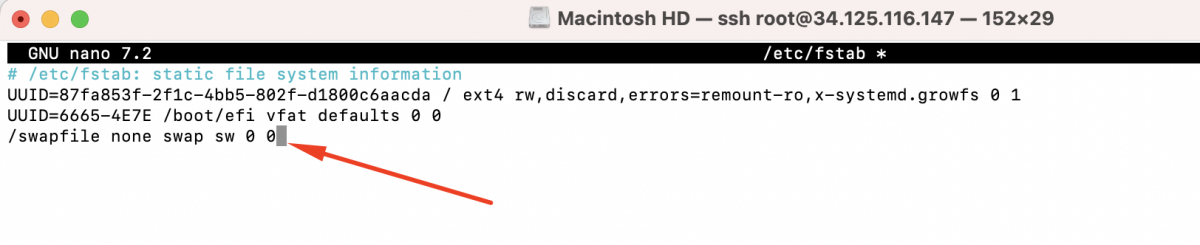
Open the /etc/fstab file in a text editor:
Add the following line at the end of the file:
Save the file and exit the text editor.
Step 9 : Verify the swap space configuration:
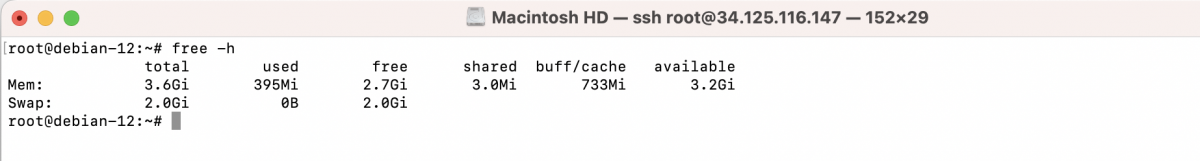
It should show the allocated swap space along with other memory information.
You have successfully created swap space on Debian 12. The swap file will be activated on system boot, and it will provide additional memory capacity when needed.