To retrieve container logs, follow these detailed steps:
Step 1 : First, run an Nginx container in detached mode so it runs in the background.
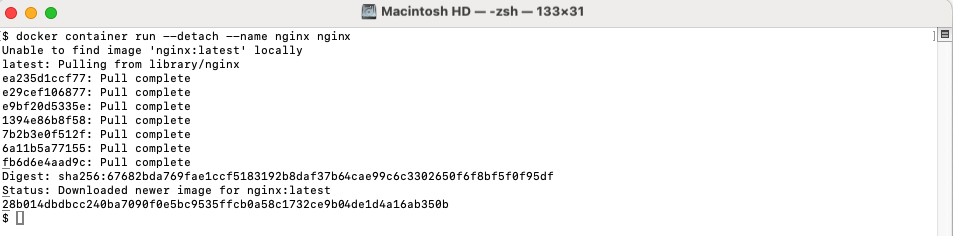
Step 2 : To see the logs produced by the container, use the docker container logs command.
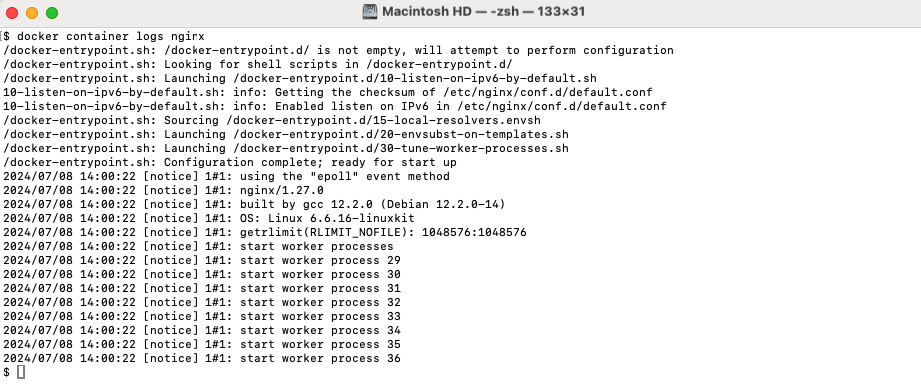
Step 3 : To view only the last few lines of the logs, use the --tail option. This example retrieves the last 5 lines.

Step 4 : To continuously monitor the logs as they are written, use the --follow option along with --tail.

To stop following the logs, press Ctrl + C.
Step 5 : After you are done, you can remove the container using the docker container rm command with the --force option to stop and remove the container.

Logging Drivers
Docker supports several logging drivers, with the default being json-file. Available logging drivers include:
none: Disables logging for the container.json-file: Logs are stored as JSON files on the host filesystem.journald: Logs are sent to journald (systemd's logging service).syslog: Logs are sent to the syslog daemon.gelf: Logs are sent to a Graylog Extended Log Format (GELF) endpoint.fluentd: Logs are sent to a Fluentd endpoint.awslogs: Logs are sent to Amazon CloudWatch Logs.splunk: Logs are sent to a Splunk endpoint.
Step 6 : You can set a specific logging driver for a container at the time of its creation. For example, to set the none logging driver:

Step 7 : After running the container, you can check the logs using:
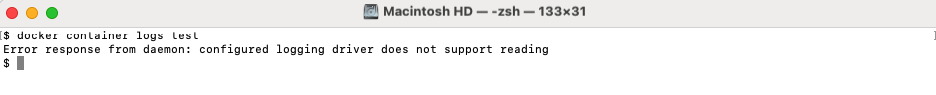
Step 8 : Remove the test container after you are done:

Changing the Default Logging Driver
To change the default logging driver for Docker on an Ubuntu 22.04 system, follow these steps:
Step 9 : Go to the Docker configuration directory.
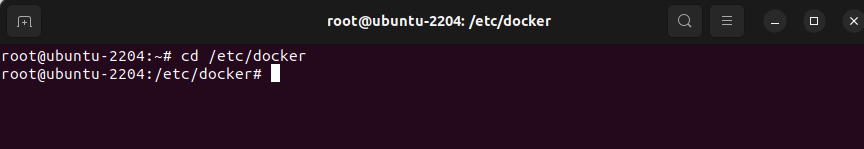
Step 10 : Open the daemon.json file in a text editor.
Add the following configuration to set local as the logging driver:
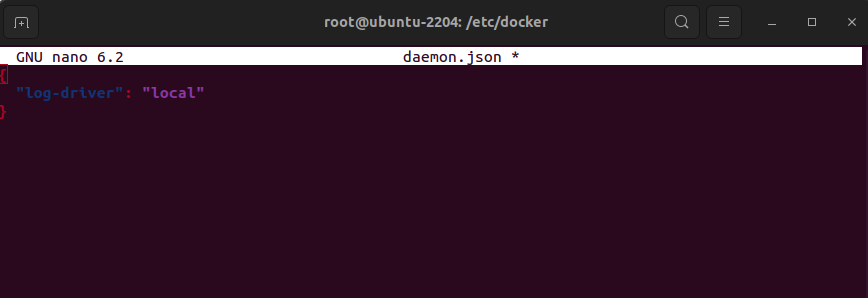
- This JSON configuration sets the default logging driver to local, which stores container logs in a custom format designed to be efficient and fast.
Step 11 : Restart Docker to apply the changes:
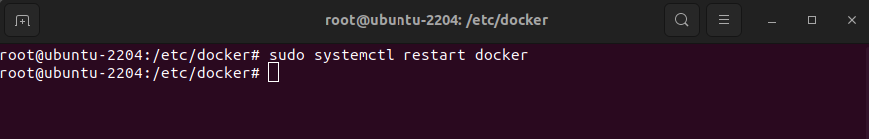
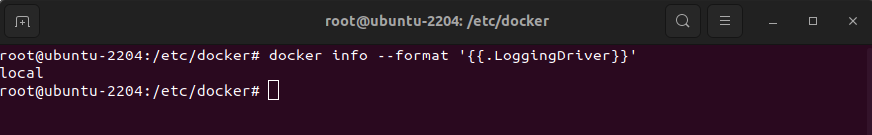
Step 12 : Check the current logging driver to ensure it has been set correctly:
Step 13 : Reopen the daemon.json file to modify the logging driver settings:
Update the configuration to set json-file as the logging driver and include additional logging options:
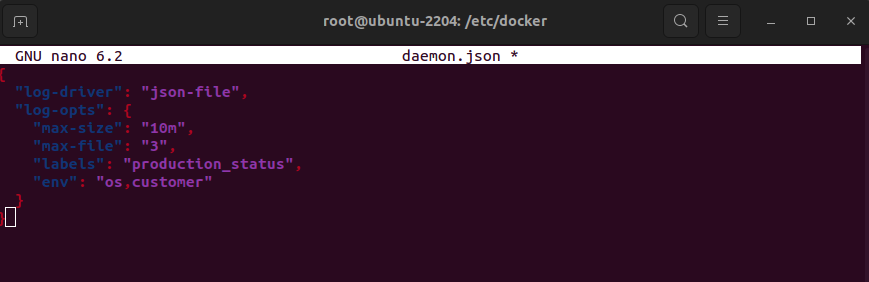
This JSON configuration sets the logging driver to json-file and includes options to rotate log files with a maximum size of 10MB and up to 3 files. It also specifies that log entries should include the production_status label and environment variables os and customer.
Step 14 : Restart Docker to apply the changes:
Step 15 : Check the current logging driver again to ensure the new settings have been applied:
Congratulations, you have successfully configured and retrieved Docker container logs!